Computing Innovation - Beneficial
Computing innovations have made things easier and simpler for many people around the world. Shopping has been revolutionized by companies like Amazon and Instacart. In addition to helping common people, computing innovation has vastly improved the medical field, while engineers and architects are able to make plans and structures much more easily.

Computing Innovation - Harmful
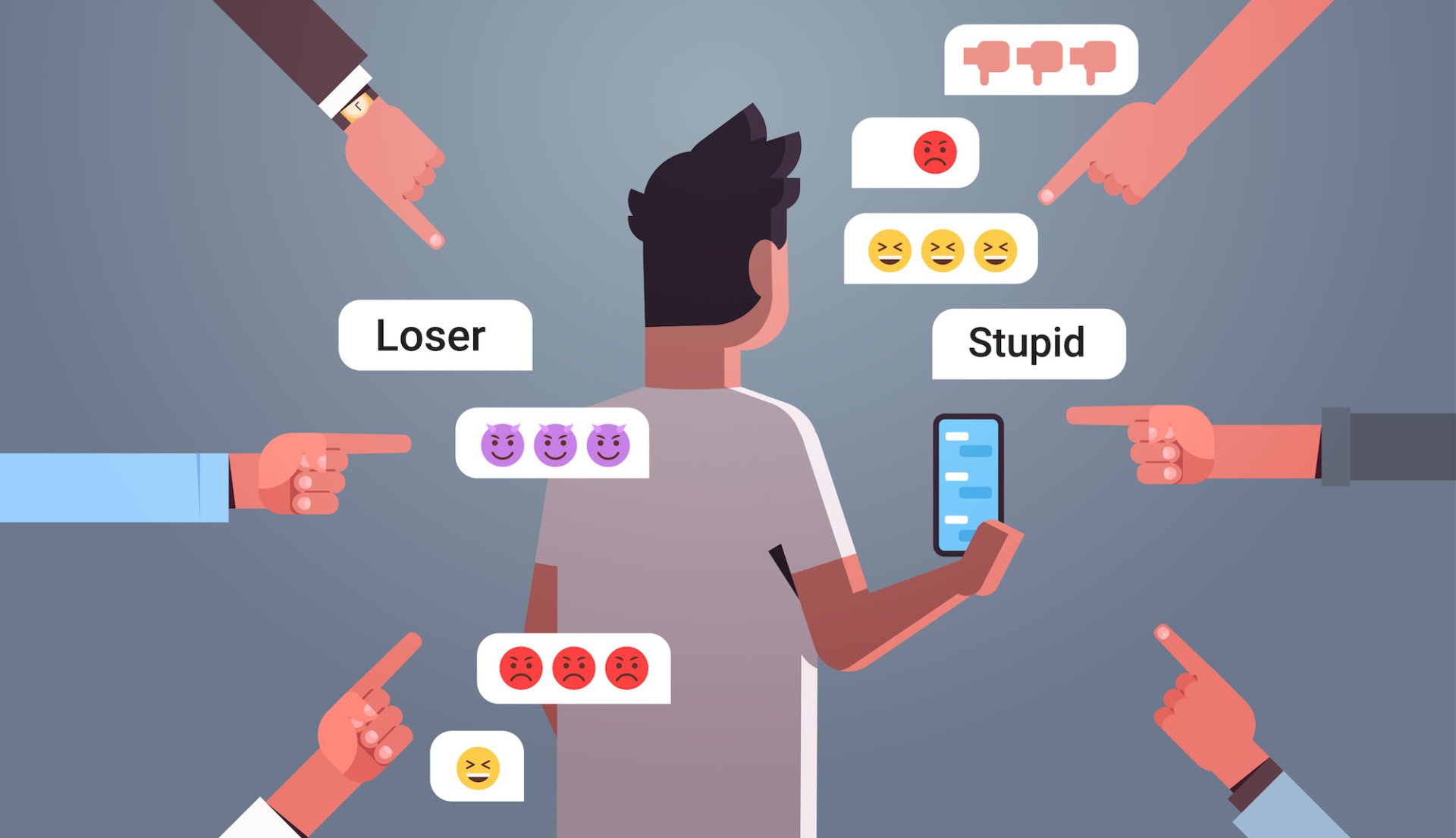
Computing innovations have also caused immense harm and suffering for many people around the world. Identity theft, cyber-bullying and deep-fakes have left the world worse off, than if technology had not been invented. Computing has also led to a loss of privacy, and a dependence on technology.

Computing Innovation - Impact Beyond
Despite innovations having positive and negative effects, these were all intentional, here are some unintentional effects of computing innovations. For example, the World Wide Web started as an advanced way for scientists to quickly share findings with others in the community and has since become what we know today. Targeted advertisement has made it easier for people to find things they want, but has the unintended consequence of collecting people's information.

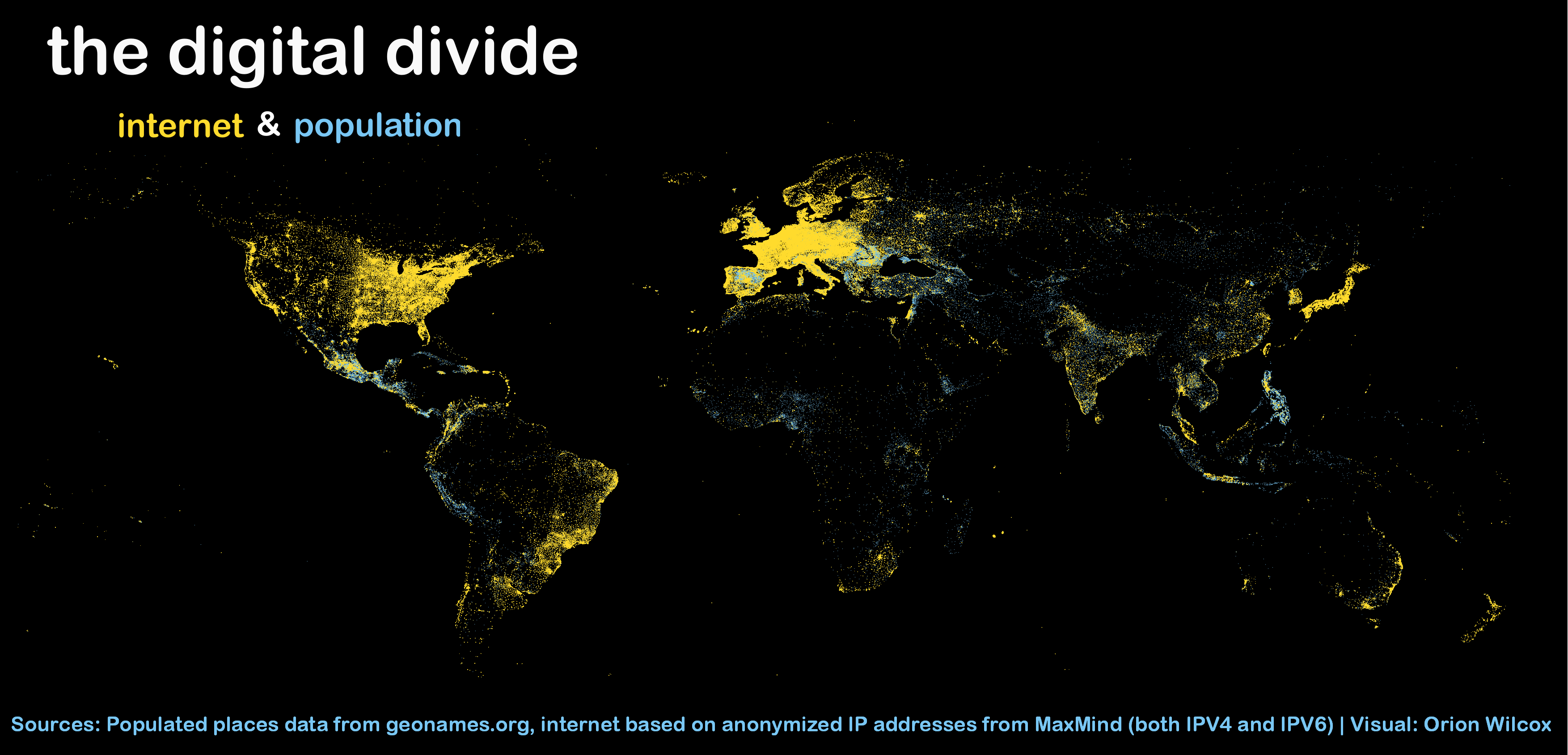
Digital Divide - The Concept
To greatly simplify what the digital divide is, the digital divide is the “a term that refers to the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology, and those that don't or have restricted access.” The early digital divide referred to the gap of people who did and did not have a landline in their house. However, now the term is more related to people who do and do not have internet access.

Digital Divide - How To Reduce
To help reduce the digital divide on the global scale, governments and international organizations, like the UN, can help raise awareness and funds to help greatly reduce the digital divide. Meanwhile on the more local scale, city and county organizations can help raise awareness and have fundraisers to help individuals in the community. Then on the school level, clubs can be created to help students from low income families get the technology they need..
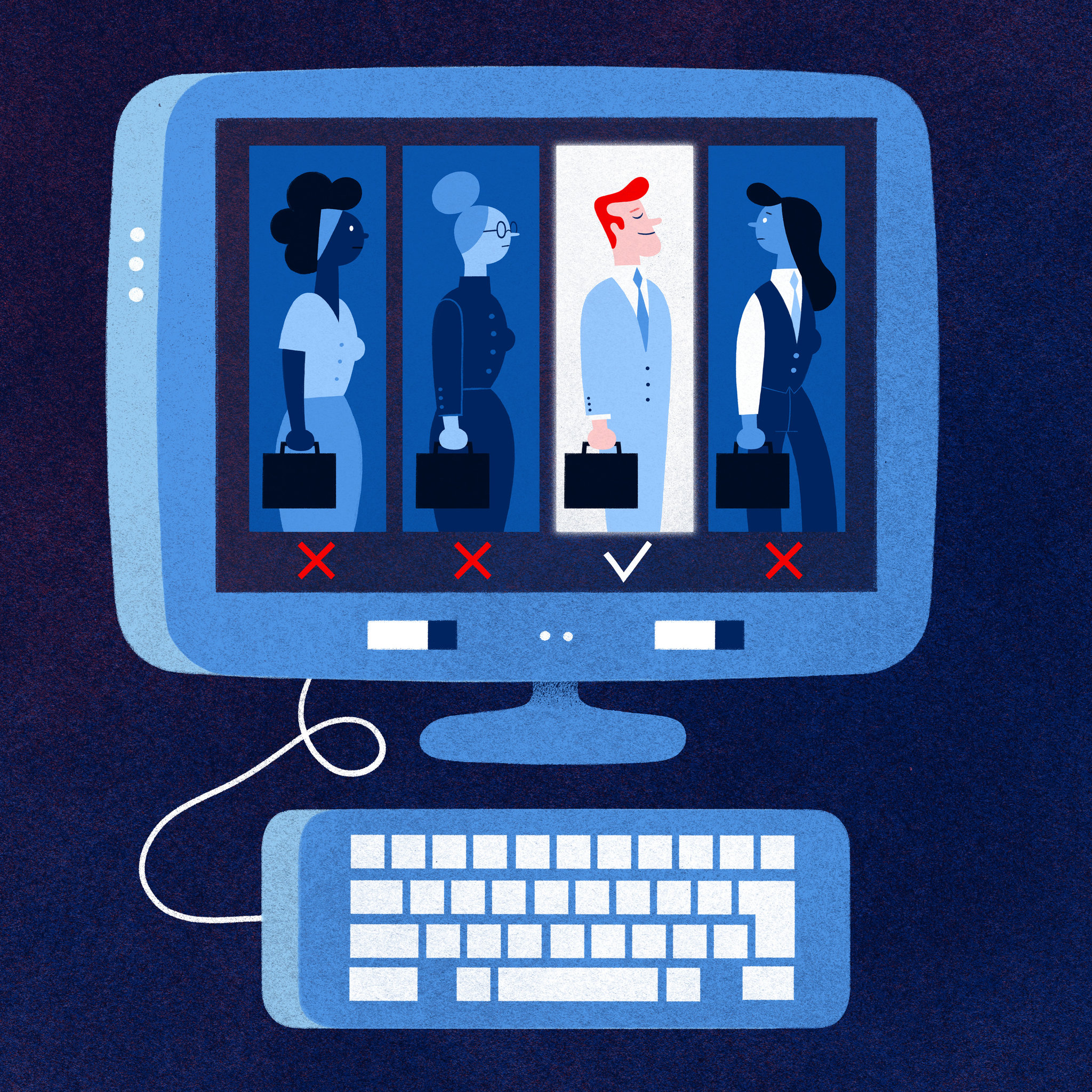
Computer Bias
Computer science in general is a bias built into a computer's algorithm. For example, criminal risk assessment algorithms can have biases against certain groups of people. Another example is with recruiting algorithms where the computer is trained to only accept certain people creating a bias in the system. To combat this bias computers need larger data sets of a large variety of people to be less biased.

Crowdsourcing - The Concept
Crowdsourcing is the collection of data from a large number of people, either with them being paid for their information or them giving it voluntarily. Crowdsourcing has many benefits in that it allows groups to better gauge what a certain bunch of people like or dislike. An example of this is when a company asks for a new logo for their company and offers a prize for the best one, this is crowdsourcing where a big company has a bunch of people compete for the best design.

Computing - Legal And Ethical Issues
Legal and ethical issues span a large range of problems in the computing world, from computer bias, to plagiarism and copyright. Plagiarism and copyright are major issues in computing, if someone plagiarizes another person’s work, they steal all the credit and profit from the original creator and if they are caught they can face serious consequences. While copyright can protect the original creator and their work, the question of how long copyright should last has been going on for a long time. So the question of what is ethical in computing remains a moving target for future people to decide.

Safe Computing
Safe computing is another large ranging idea in the computing world. It is important to stay protected from viruses, malware, and phishing attempts which can all steal your data. Safe computing can also involve social media and thinking before you post, as well as knowing that browsers and websites have cookies that can also take your data. You can protect yourself from these things, by installing a firewall, always using secure internet and by making sure you only download things from trusted sites.
